1
ExpectedSpeech/LanguageMilestonesbyAge
Age Syntax Semantics Morphology Pragmatics
3–4
- Averages4‐wordspersentence
- Usesmostlycompletesentences
- Usesmostlynouns,verbsand
personalpronouns
- Usesnegation(e.g.:“Idon’twant
it”)
- Usesclausecoordinatingdevices
(i.e.:and,because)
- Labelsmostthingsinenvironment
- Relatesexperiencesandtellsabout
activitiesinsequentialorder(e.g.:
wewenttothestore.Webought
someapplesandthenwecame
home)
- Understandssomecommon
opposites(little/big,fast/slow)
- Cansingafamiliarsong(twinkle,
twinklelittlestar)
- AnswersquestionssuchasWhic
h
one,whereis,whatdoyouhave
- Understandsagent/action(e.g.tell
mewhatflies,swims,bites)
- By48monthscancomplete
oppositeanalogies(daddyisaboy,
mommyisa______)
- Understandsmostpreschool
children’sstories(by48months)
- Understandsconceptsempty/full,
big/little,more/less,infro
nt/in
back,nextto)
- UsespronounsI,me,you,they,us
- Usesthirdpersonsingular,
presenttense(e.g.,heruns)
- Consistentlyusessimple(regular)
pastandpresentprogressives(is
running)
- Usesis(heishappy),are(weare
happy),andam(Iamhappy)in
sentences
- Usesregularpluralforms
correctly
- Usespossessivemarkers(e.g.:
“Theboy’sclothes”)
- Usescommunicativefunctions
including:
- Requ
esting(canIhavejuice,
whereismommy)
- Protesting(Idon’t’wantthat)
- Greetings
- Roleplaying
- Respondswithstructuressuchas
yes,no,because
- Engagesinconversationforat
least3exchanges
4–5
- Averages5‐6wordspersentence
(e.g.,Ihavethatatmyhouse)
- Understandsandusescomplex
sentences(e.g.,Ihurtmyself
becauseIfelldown)
- Usesfuturetense(e.g.,shewill
gotothestore)
- Usesmostpronounsincluding
possessives
- Cannameitemsinacategory(e.g.,
food,animals)
- Useswhyandhowquestions
- Answerswimplewhenquestions
(e.g.,whendoyousleep)
- Candefinecommonwords(e.g.,
whatisahat)
- Identifyobjectbyuseandfunction
(e.g.whatdoyoucu
twith)
- Asksmeaningofwords
- Cangivewholename
- Usesmorphologicalmarkersfor
plurals(shoes),possessives
(mommy’s)adtensemarkers
(jumped,jumping,jumps)
- Usescomparatives(big,bigger,
biggest)
- Usesirregularpluralsfairly
consistently(mice,teeth)
- Modifiesspeechasafunctionof
listenerage
- Maintaintopicoversuccessive
utterancesformorethan3turns
2
Age Syntax Semantics Morphology Pragmatics
4‐5
Averages6wordspersentence
Speaksincompletesentencesby5
Canusefuturetense(e.g.,“Shewill
gotothestore”)
Canuseif,soinsentences
Usesconcretemeaningsandwords,
butrespondstosomeabstract
ideasappropriately
Canpointtocategoricalitems(e.g.,
pointtoallthefruit)
Canname3‐4itemsinacategory(e.g.,
food,animals).
Canusemostpronouns,including
possessives(e.g.,mine,his,her)
Canusewhyandhowforan
explanation
Canusewhatdo/didinqu
estions
Answerssimple“when”questionslike
“whendoyousleep)
Retellssimple,3‐sequncestories
Cangivefirstandlastname
Canidentify10commonwordsbyuse
and/orfunction(e.g.,ifdirected,
“Showmewhattellstime,”“Show
mewhichonegivesusmilk)
Candefine10commonwordsby
function
Usescomparatives(e.g.,bigger,
nicer,taller)
Canusecould,wouldinsentences
Usesregularpluralswithgeneral
consistency
Canmaintaintopicoftheir
choosingoversuccessive
utterances
Oftenusesegocentricmonologue
(thismonologuedoesnot
communicateinformationto
thelistener)
Beginstotelljokesandriddles
(around5years)
3
Age Syntax Semantics Morphology Pragmatics
5–6
Canusepresent,pastandfuture
tense
Usestheconjunction‘and’tostring
wordstogether(e.g.,“Abearand
awolfandafox”)
Canuseauxiliaryhavecorrectlyat
times(e.g.,‘Ihavethecookie’)
Followsnoveldirectionscontaining
spatialrelationsandprepositions
suchasontop,behind,far,near
(e.g.,“standbehindthechair”)
Candistinguishalike,same,different
Cangivenmostofaddress
Identifiesmostcommonopposites
(e.g.,hard‐soft,fat‐thin,high‐low);
understands“oppositeof”(e.g.,
“What’stheoppositeofcold?”)
Candefinesobj
ectsbyuseand
composition(e.g.,“Napkinsare
madeofpaper;youwipeyour
mouthwiththem”)
Cantellstories;retellstalesofpast
andpresentevents
Cananswer“Whathappensif…?”
questions
Understandsconceptssuchas
yesterday‐tomorrow,more‐less,
some‐many,several‐few,most‐
least,before‐after,now‐later(e.g.
,
whathappensafterlunch?)
Canstatesimplesimilaritiesand
differencesofobjectswhen
presentedwithpictures
Comprehendsfirst,last
Cannamepositionofobjects:first,
second,third(emerging)
Cannamedaysoftheweekinorder
Knowsfunctionsofbodyparts
Canidentifysomeindefinite
pronounsincludingany,every,
both,few,many,eachand
othersemerging
Useofirregularpluralsemerging
Canusepossessivesandnegatives
consistently
Usesallpronounsconsistently
Canusesuperlative–est(e.g.,
smartest)
Beginstouseadverbialword
endings(e.g.,‐ly)
Understandshumor,surprise
Canrecognizeasociallyof
fensive
messageandreworditinpolite
formwhencued
Beginstouseandunderstand
formallevelsofaddress(e.g.,
Mr.,Mrs.)
Candifferentiate80%ofthetime
betweenpoliteandimpolite
utterances
Usesexpressionssuchas“thank
you”and“I’msorry”
Oftenaskspermissiontouse
objectsbelongingtoothers
Contributestoadultconve
rsation
withfamiliaradults
4
Age Syntax Semantics Morphology Pragmatics
6–7
Beginstousecauseandeffect
(e.g.,IfIdomywork,Igeta
sticker)
Usesreflexivepronouns(e.g.,
himself,myself)
Canusepassivevoice
Emerginguseofembedding(e.g.,
“Thegirlwhoboughtthedress
wenttotheparty”)
Canuseadverbialconjunctions
now,then,so
Understandstheseasonsofthe
yearandkno
wswhatyoudoin
each
Distinguishesrightandleftinself,
butnotinothers
Usesmostmorphologicalmarkers
fairlyconsistently(e.g.,Thetwo
boys
walkedtothestore)
Emerginguseofirregular
comparatives(good,better,best)
Continuestoimprovecorrectuse
ofirregularpasttenseandplurals
Beginstoproducegerunds(anoun
formproducedbyadding–ing
toaverbinfinitive,e.g.,fish,
fishing–Fishingwithmydadis
fun)
Acquiresuseofderivatio
nal
morphemes,inwhichverbsare
changedintonouns(e.g.,catch
becomescatcher)
Becomesawareofmistakesin
otherpeople’sspeech
Isapttouseslang(e.g.,“that’s
cool”)
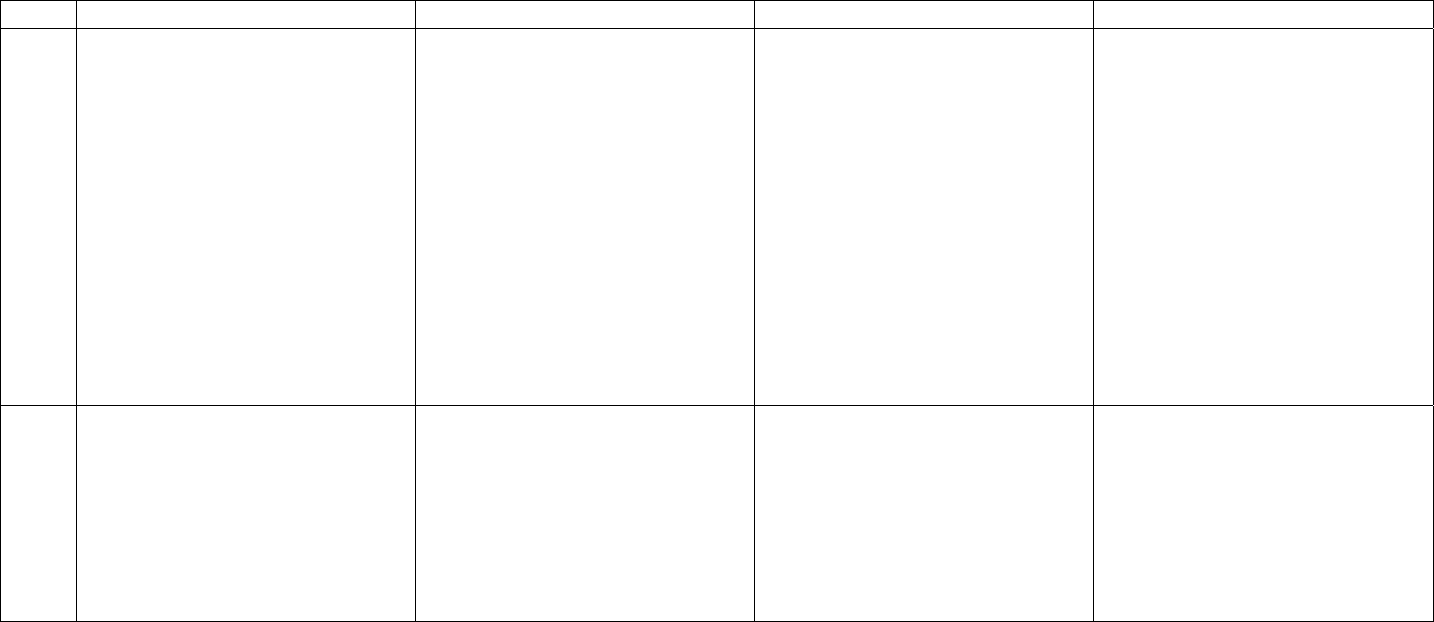
7–8
Canuseconjunctionstoelaborate
onsentencestructure(e.g.,and,
but,or,because)
Makesapredictionaboutstories
Understandinganduseof
figurativelanguageemerging
Usesdetailsindescription(e.g.“I
seeablackcatsittingonthe
roundtable”)
Createsconversationsuggestedby
apicture
Enjoystellingstoriesand
anecdotes
Retel
lsastory,keeping3+events
insequence
Usesmostirregularverbforms,
althoughwithsomemistakesin
irregularpasttense(e.g.,
“yesterdayhebrokedthevase”)
Usessuperlatives(biggest,
prettiest–“thebiggestdogwon
therace”)
Usesadverbsregularly(e.g.,“He
ranquickly”)
Initiatesandmaintains
conversation
Is
abletorole‐play,tota
kethe
listener’spointofview
Determinesandusesappropriate
discoursecodesandstyles(e.g.,
informalwithfriends,formal
withadults)
Usesnonlinguisticandnonverbal
behaviors–posture,gestures–
appropriately
Cansustainatopicwithan
individualsorsmallgroup
throughanumberof
conversationalturns,bu
ttopics
tendtobemoreconcrete
5
Age Syntax Semantics Morphology Pragmatics
8‐9
Comprehendsandusestelland
promise
Hasgenerallycompletedmostof
syntagmatic‐paradigmaticshift
Beginstointerpretpsychological
statesdescribedwithphysical
terms(cold,blue)but
misinterprets
Uses–ersuffixtomarkinitiatorof
anaction(teacher)
Usesfullpassives(80%ofchildren)
Sustainsconcretetopics
Recognizesnonliteralm
eaningsin
indirectrequests
Beginsconsideringothers’
intentions
Isabletojudgegrammatical
correctnessseparatefrom
semantics
Sustainstopicsthroughseveral
turns
Addressesperceivedsourceof
breakdowninrepair
Producesallelementsofstory
grammar
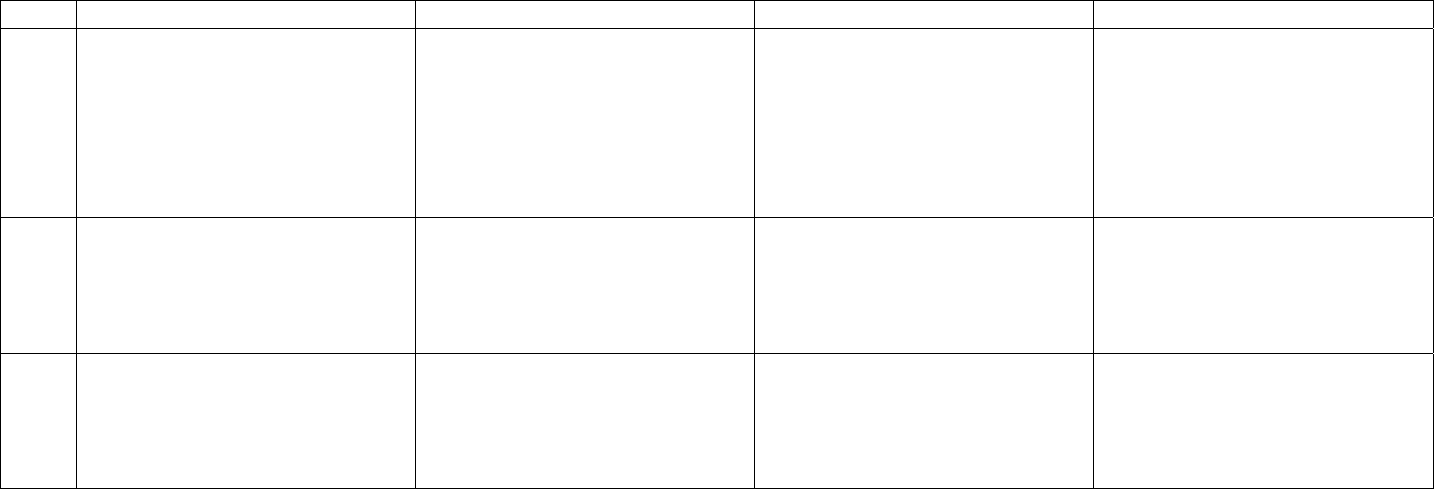
10‐11
Comprehendsandusesask
Comprehendsbecauseconsistently
Understandsdifferencesbetween
definitely,probably,andpossibly
Createsmuchwithmassnouns
Comprehendsifandthough
Comprehendsinandonusedfor
temporalrelations
Comprehendsmostfamilialterms
Createsabstractdefinitions
Hasallelementsofconventional
adultdefinitions
Understandspsychologicalstates
describedwithphysicalterms
Usespronounstorefertoelements
outsidei
mmediatesentence
Uses–erforinstrument(eraser)
Sustainsabstracttopicsin
conversation
6
Age Syntax Semantics Phonology/Metlinguistics Pragmatics
11‐12
UnderstandsIF‐Though (e.g.Ifthe
busislate,Iwillbelatefor
school.Ilikeyouthoughmy
motherdoesn’t)
Canexplainrelationshipsbetween
meaningsofmultiplemeaning
words(e.g.Iatethesandwich,
Theacidatethemetal)
Mostcommonidioms understood
(e.g.Don’tcountyourchickens
beforeth
eyhatch)
Metacognitiveskillsemerge(e.g.
definewords,editanother’s
writing)
Understandsjokesandriddles
basedonlexicalambiguity(e.g.
ThegolfersaidduckandIsaid
“where”)
12‐14
Useofperfectaspect(e.g.
have/had+verb)increases(e.g.
Hehadbeentotheparkbefore)
Canexplainmeaningsofproverbsin
context(e.g.Achainisasstrongas
it’smissinglink)
Abstractdictionarydefinitionsgiven
forwords
Knowledgeofstressrules(e.g.
yellowjacketvs.yellowjacket)is
acquired
Understandsjokesandriddles
basedondeepstructure
ambiguity(e.g.Itwasraining
catsanddogsandIsteppedina
poodle)
15‐18
Fulladultrangeofsyntactic
constructionsreached(e.g.all
verbtenses,transitionwords,
adjectivesandadverbs,etc)
Averagevocabularysizeofhigh
schoolgraduateis10,000words
Languageisusedtomaintainsocial
bonds(e.g.justtalking)
Sources:
Paul,R.,Language Disorders from Infancy through Adolescence: Assessment and Intervention. (3
rd
Ed),. St. Louis: Mosby, 2007.
Roseberry‐McKibbin,C.&HegdeM.N.,AnAdvanced ReviewofSpeech‐LanguagePathology:PreparationforPRAXISandComprehnsiveExamination(2
nd
Ed.),
Austin:Pro‐Ed,2006.
